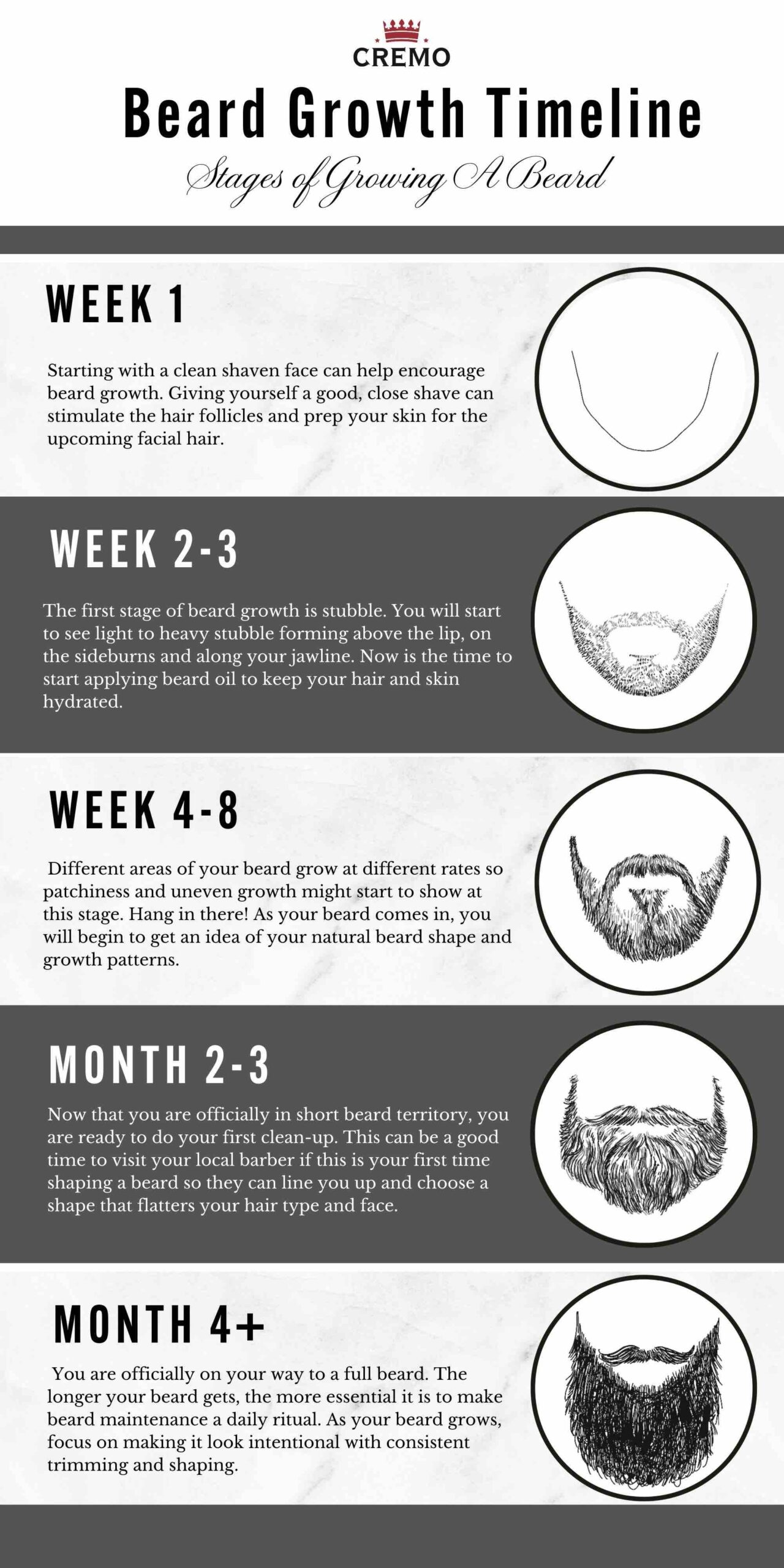
If you’ve ever wondered about the curious phenomenon of men who can’t grow facial hair, you’re not alone. Whether it’s due to genetic factors or simply their body’s way of expressing itself, there is a significant portion of the male population who find themselves without a stubble to call their own. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at this intriguing issue and explore the various factors that contribute to the absence of facial hair in some men. Buckle up and let’s embark on this journey to understand the mysteries behind men who can’t grow facial hair!
Causes of Inability to Grow Facial Hair
Having a full beard or a well-groomed mustache is often seen as a symbol of masculinity and can enhance one’s physical appearance. However, not all men are blessed with the ability to grow facial hair easily. If you find yourself in this situation, it’s essential to understand the various factors that can contribute to this inability. Here, we will explore the genetic factors, hormonal imbalance, medical conditions, age, and stress and lifestyle factors that may prevent you from growing facial hair.
Genetic Factors
One of the primary reasons some men struggle to grow facial hair can be traced back to their genetic makeup. Genetics plays a crucial role in determining not only your physical characteristics but also the patterns of hair growth on your face. Each individual inherits a combination of genes from their parents, and these genes determine how your facial hair will develop.
Role of Genetics in Facial Hair Growth
The genes you inherit from your parents can influence the density, color, and texture of your facial hair. If your father and other male relatives have facial hair, there is a higher chance that you will also be able to grow it. On the other hand, if your family has a history of limited facial hair growth, it is likely that you may face the same challenges.
Androgen Receptor Gene (AR Gene)
The function of the androgen receptor gene (AR gene) is crucial in the process of hair growth. Androgens, such as testosterone, bind to the androgen receptors in hair follicles, stimulating facial hair growth. Any variations or mutations in the AR gene can lead to decreased sensitivity to androgens, resulting in sparse or patchy facial hair growth.
Ethnicity and Facial Hair Growth
Ethnicity also plays an important role in facial hair growth patterns. Certain ethnicities, such as individuals of Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and South Asian descent, tend to have thicker and more abundant facial hair. On the contrary, people with East Asian or Native American heritage may experience sparser facial hair growth. These differences can be attributed to genetic factors specific to various ethnic groups.
Hormonal Imbalance
Hormones, particularly testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are instrumental in the development and growth of facial hair. Any hormonal imbalances in the body can interfere with this process and hinder facial hair growth.
Testosterone and Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Testosterone, an androgen hormone, plays a crucial role in promoting hair growth. This hormone is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by an enzyme known as 5-alpha reductase. DHT is a more potent form of testosterone and is responsible for stimulating hair follicles on the face. If there is an imbalance in testosterone or DHT levels, it can lead to inadequate facial hair growth.
Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism refers to a condition where the body produces inadequate amounts of testosterone. This hormonal deficiency can affect the development of secondary sexual characteristics, including facial hair. Apart from limited facial hair growth, symptoms of hypogonadism may include decreased muscle mass, reduced libido, and fatigue.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can disrupt the balance of hormones in the body. Both conditions can lead to hair loss and affect the growth of facial hair. Proper diagnosis and management of thyroid disorders are crucial to restoring hormonal balance and potentially improving facial hair growth.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can directly impact facial hair growth. If you are struggling to grow facial hair, it is essential to consider the possibility of an underlying medical condition.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that causes hair loss in patches. While it primarily affects the scalp, it can also lead to the loss of facial hair. Individuals with this condition may experience smooth, hairless patches on their face, inhibiting the ability to grow a full beard or mustache.
Klinefelter Syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by the presence of an extra X chromosome in males. This condition can lead to decreased production of testosterone, resulting in limited facial hair growth. Other symptoms may include infertility, breast development, and reduced muscle mass.
Cushing’s Syndrome
Cushing’s syndrome is a hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol. Cortisol is a hormone that regulates various bodily functions, including hair growth. Excessive cortisol production can result in hair loss, including facial hair. Individuals with Cushing’s syndrome may experience thinning or absence of facial hair as a consequence.
Pituitary Disorders
The pituitary gland is responsible for producing and regulating several hormones, including those involved in hair growth. Disorders affecting the pituitary gland, such as tumors or dysfunction, can disrupt hormone production and affect facial hair growth. Proper medical intervention and treatment are necessary to address these underlying conditions.
Age
As men age, changes in facial hair growth patterns are not uncommon. The inability to grow facial hair can be a natural consequence of the aging process.
Age-Related Changes in Facial Hair Growth
It’s important to recognize that facial hair growth may vary throughout different stages of life. During adolescence and early adulthood, hormonal changes typically lead to an increase in facial hair. However, as men enter their late twenties or early thirties, facial hair growth may stabilize or even decline. This decrease in facial hair growth is a natural part of the aging process for some individuals.
Delayed or Late Puberty
Delayed or late puberty can also contribute to the lack of facial hair growth. Puberty is the period during which hormone production increases, leading to the development of secondary sexual characteristics, including facial hair. In some cases, individuals may experience delayed onset or slower progression of puberty, resulting in delayed facial hair growth.
Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Not all causes of inability to grow facial hair are directly related to physical factors. Stress and certain lifestyle choices can also impact facial hair growth.
Effects of Chronic Stress on Hair Growth
Chronic stress can have adverse effects on overall health, including hair growth. High-stress levels can disrupt hormonal balance, potentially affecting facial hair growth. It is essential to manage stress effectively through relaxation techniques, exercise, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits
Unhealthy lifestyle habits, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition, can hinder facial hair growth. Smoking can damage hair follicles, impede blood flow to the face, and affect the health of hair follicles. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to nutrient deficiencies, which can impact the quality and growth of facial hair. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals is vital for supporting healthy hair growth.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Certain nutrients are essential for healthy hair growth, including facial hair. Inadequate intake or deficiencies in vitamins A, C, D, E, B vitamins, zinc, and iron can hinder facial hair growth. A well-balanced diet, including nutrient-rich foods, can help provide the necessary vitamins and minerals needed for optimal facial hair growth.

Psychological Impact of Inability to Grow Facial Hair
The inability to grow facial hair can have significant psychological implications for men. It is essential to address the emotional impact and provide support for those dealing with this issue.
Societal Expectations and Masculinity
Societal expectations often associate facial hair with masculinity and maturity. Men who struggle to grow facial hair may feel pressure to conform to these expectations, leading to feelings of inadequacy or self-consciousness. It is crucial to challenge societal norms and recognize that masculinity is not solely defined by the presence of facial hair.
Body Image and Self-Esteem
Facial hair can play a role in an individual’s perception of their own physical attractiveness. Men who are unable to grow facial hair may experience diminished self-esteem or negative body image. It is important to foster healthy self-esteem and focus on the qualities that make you unique and confident, regardless of facial hair.
Psychological Distress and Depression
In some cases, the inability to grow facial hair can lead to psychological distress or contribute to symptoms of depression. Feelings of sadness, frustration, or social isolation are not uncommon. Seeking psychological support and counseling can provide a safe and supportive environment to address these emotions and develop healthy coping strategies.
Treatments and Solutions
While growing facial hair naturally may not be possible for everyone, there are various treatments and solutions available to promote facial hair growth and address the underlying causes.
Genetic Counseling and Testing
For individuals with genetic factors impacting facial hair growth, genetic counseling and testing may provide valuable insight. Genetic counselors can assess family history and genetic factors, offering personalized guidance and recommendations for managing expectations and understanding the limitations.
Hormone Replacement Therapy
In cases where hormonal imbalances are the primary cause of limited facial hair growth, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be considered. HRT involves replacing deficient hormones in the body to restore hormonal balance and potentially stimulate facial hair growth. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the suitability and potential risks associated with HRT.
Dermatological Treatments
Dermatological treatments, such as minoxidil, can be used topically to stimulate hair follicles and promote facial hair growth. Minoxidil is an over-the-counter medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of hair loss. However, it is important to consult with a dermatologist before using any topical medications to ensure appropriate usage and potential side effects.
Psychological Support and Counseling
The emotional impact of the inability to grow facial hair should not be underestimated. Seeking psychological support and counseling can provide a safe space to explore and address the psychological distress associated with this issue. A trained therapist can offer coping strategies, promote self-acceptance, and provide guidance for navigating societal pressures.
Facial Hair Alternatives for Men
For those unable to grow facial hair or looking for alternative options, there are several methods and techniques available to achieve the desired facial hair appearance.
Facial Hair Transplants
Facial hair transplants offer a surgical solution for individuals who wish to have a fuller beard or mustache. This procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from other parts of the body to the face, creating a natural-looking beard or mustache. It is essential to consult with a qualified surgeon to discuss the potential risks, benefits, and suitability of this procedure.
Topical Medications
In addition to minoxidil, there are other topical medications available that claim to promote facial hair growth. These medications often contain a combination of vitamins, minerals, and botanical extracts that are thought to nourish hair follicles and stimulate growth. It is important to exercise caution and consult with a dermatologist before using any topical medications to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Beard and Mustache Grooming Techniques
Even if you can’t grow a full beard or mustache, there are grooming techniques that can enhance the appearance of facial hair. Trimming and shaping the existing hair can create the illusion of a fuller beard or mustache. Experimenting with different styles and lengths can help find a look that suits your facial features and personal preference.
Conclusion
The inability to grow facial hair can be attributed to a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, age, and lifestyle influences. Understanding these underlying causes and seeking appropriate solutions can help individuals navigate the emotional and physical challenges associated with limited facial hair growth. Whether through genetic counseling, hormone replacement therapy, dermatological treatments, or psychological support, there are options available to promote facial hair growth, enhance self-esteem, and embrace one’s unique masculinity. Remember, the presence or absence of facial hair does not define your worth or masculinity – it’s your character and inner confidence that truly matters.